_EXCLUSION ZONE & VORTEX TECHNOLOGY_
Exclusion Zone & Vortex Technology
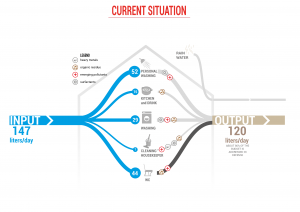
The rapid evolution of the worldwide scenario, the climate change, biodiversity loss, resources depletion and rapid technological and social development called for a radical response from the design community. Anthropogenic pressures on the Earth System have reached a scale where an urgent change of route towards sustainability is inescapable. At the same time, the understanding of the raising complexity in natural and social systems, resulting by the discoveries occurred during the last century in Physics, Cybernetics, Biology, etc. made the reductionism view inadequate. Therefore, the Systemic Design (SD) methodology results as a supportive tool for helping the designer to look at the objective in its complexity and to organize all the actors of the project by giving them the ability to relate and evolve autonomously. As a consequence the individual parts of the system are intertwined, forming a virtuous network (autopoietic) of relations between the flows of matter, energy and information. The application of the SD methodology to the design of a water treatment entailed a focus on the understanding of the water behavior both at molecular and at macroscopic level. The SD methodology drove the research through an intense exploration of the complex properties of liquid water touching a variety of disciplines from physics to chemistry until bioengineering and medicine that has opened the frontiers to a more holistic understanding of water. As a consequence we got in touch with some of recent theories from physics, biology and biochemistry, that have cast a light on some new properties and behaviors of water able to dramatically change the perspective on which we use to consider this incredible resource.
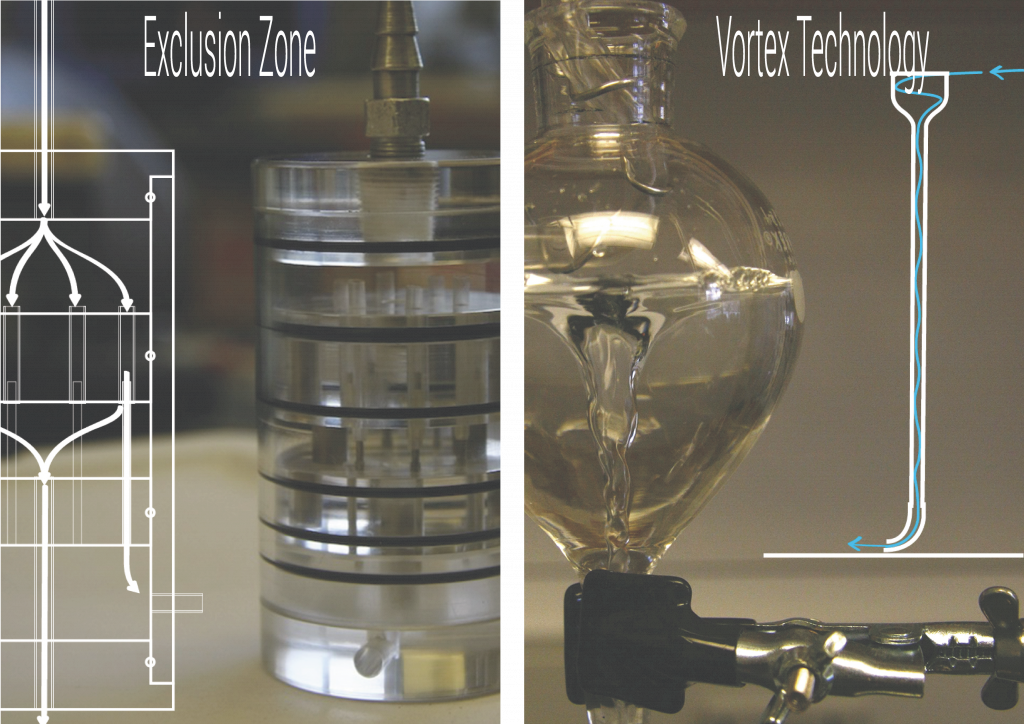
The Exclusion Zone (EZ) is an interfacial water region that has a lower concentration of solutes than in the bulk water. Moreover water in the EZ was observed to have physico-chemical characteristics (e.g., light absorption, fluorescence, higher viscosity and birefrigence) that distinclty differed from those of the bulk water. The long-range effect of a hydrophilic surface on a colloidal suspencion has not been well recognized until recently. Zheng and Pollack (2003) reported the exclusion of colloidal particles near hydrophilic surfaces, which left a clear water region several hundred micrometers from the surface. Thanks to the collaboration with Professor G.H. Pollack we have developed few prototypes with the aim to collect the EZ water fraction. The efficiency of prototypes has been tested at the SMAT Research Center. The water filtration system based on the EZ phenomenon is highly innovative since it does not require the use of external energy (beside radiant energy) and physical barriers. Activities carried out in collaboration with:
– SMAT Research Center (Turin – Italy) ;
– Pollack Laboratory at the Bioengineering Department at the University of Washington (Seattle – US).
- Vortex Technology, it is based on the ability of water to self-organize in a free vortex that affects the physical/chemical characteristics of water compared to that of bulk water. Thanks to the collaboration with the IET, we made some prototypes to test the physical separation of suspended solids. The positive results achieved allow us to hypothesize the use of this technology, wich does not require mechanical handling and therefore energy, as a pretreatment before the water purification process. In addiction, we have experienced a tangible benefit (in term of dry mass, and time of growth) in plant growth by using the water treated with vortex.
Activities carried out in collaboration with:
– Institute of Ecological Technology (Malmo – Sweden).Reference: Toso Dario (2015), Visione Sistemica dell’Acqua. PhD Thesis
– Research TEAM –
Coordinator: Silvia Barbero and Luigi Bistagnino
Team: Dario Toso and Alessio Ferru
– YEAR –
2014-2017